I only recently came across this type of data architecture and to fair I have been using it without even realising that it had a specific type of name to it. I was actually asked about this during an interview and I was immediately stunned as I usually have an inclination to what something is particularly when it comes to data warehouse or data lakes. I previously had worked on architecture which involved batch and realtime data using aurora for OLTP and snowflake for OLAP which I shall cover on a later date.
Lambda Architecture is a data-processing design pattern that combines batch processing and real-time stream processing to provide both scalability and low-latency insights.
It was introduced to solve the challenge of balancing:
Accuracy & completeness (batch layer)
Speed & freshness (speed/streaming layer)
This dual-layer model ensures businesses can react to real-time events while still maintaining a “single source of truth” with historical data.
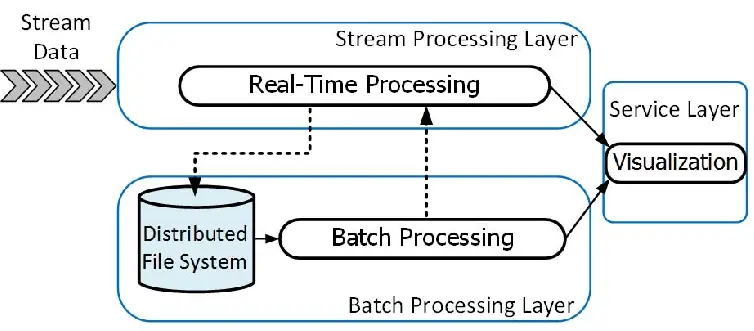
Batch Layer
Stores the master dataset (immutable, append-only raw data).
Uses distributed storage (e.g., HDFS, Amazon S3, Snowflake).
Periodically recomputes views or models to guarantee accuracy.
Speed (Streaming) Layer
Processes real-time events as they arrive.
Provides low-latency updates.
Typically powered by stream processing tools like Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis, Apache Flink, or Spark Streaming.
Serving Layer
Combines outputs from batch and speed layers.
Serves query responses with both historical (batch) and real-time (streaming) data.
Backed by fast-access databases (e.g., Cassandra, DynamoDB, Elasticsearch, or Snowflake for analytics).

Batch layer databases:
Hadoop HDFS
Amazon S3
Snowflake (cloud-native warehouse with time-travel & micro-partitions)
Azure Data Lake
Streaming layer databases & queues:
Apache Kafka
AWS Kinesis Data Streams
Google Pub/Sub
Serving layer databases:
NoSQL (Cassandra, HBase, DynamoDB) for key-value lookups
Elasticsearch for search queries
Snowflake/Redshift/BigQuery for analytics & BI
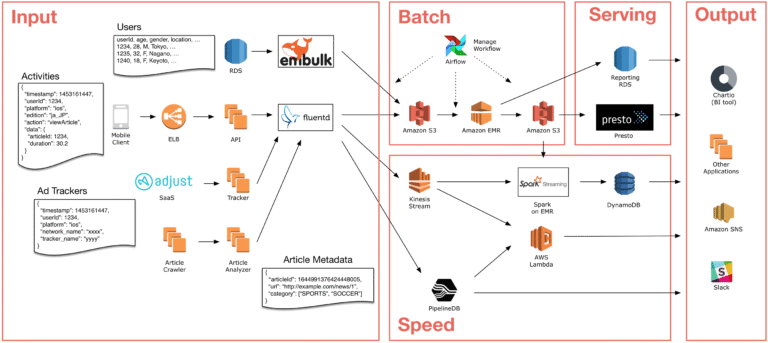
Data Ingestion
Sources: IoT devices, transactional DBs, application logs, clickstreams.
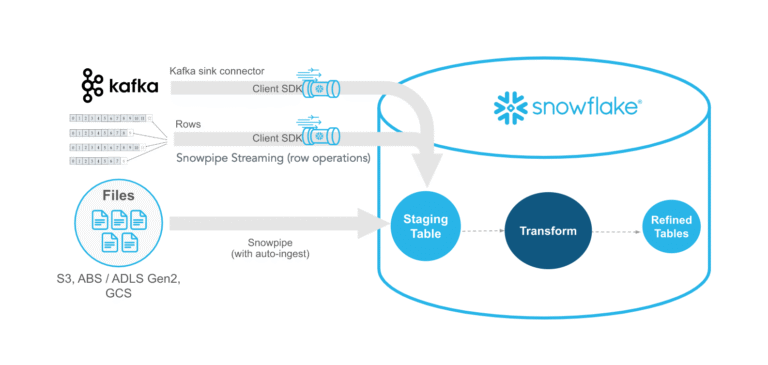
Tools: Kafka Connect, AWS Glue, Snowpipe (for continuous ingestion into Snowflake).
Processing
Batch: MapReduce, Apache Spark jobs, dbt in Snowflake.
Streaming: Apache Flink, Spark Streaming, AWS Kinesis Analytics, Kafka Streams.
Storage
Raw immutable storage in data lakes or warehouses.
Real-time state management in fast NoSQL databases.
Serving & Querying
BI dashboards (Tableau, Power BI, Looker).
Real-time applications (fraud detection, recommendation engines).
Recommendation engines: Personalization using both historical profiles and live activity.
Log and clickstream analytics: Tracking user activity at scale.
Financial systems: Low-latency decision-making with guaranteed accuracy over time.
Complexity: Two different code paths (batch & streaming) increase maintenance overhead.
Data consistency: Reconciling batch vs. real-time results can be challenging.
Cost: Running both real-time and batch infrastructure doubles resource needs.
Modern Cloud Approach:
Platforms like Snowflake and Databricks now unify batch + streaming in one architecture.
Tools like Snowpipe, Streams, and Tasks allow incremental and continuous loading without maintaining two separate layers.